Multi-task Multi-view Learning
Jia He, Changying Du, Fuzhen Zhuang, Xin Yin, Qing He, Guoping Long: Online Bayesian max-margin subspace learning for multi-view classification and regression. Mach. Learn.2020.
-
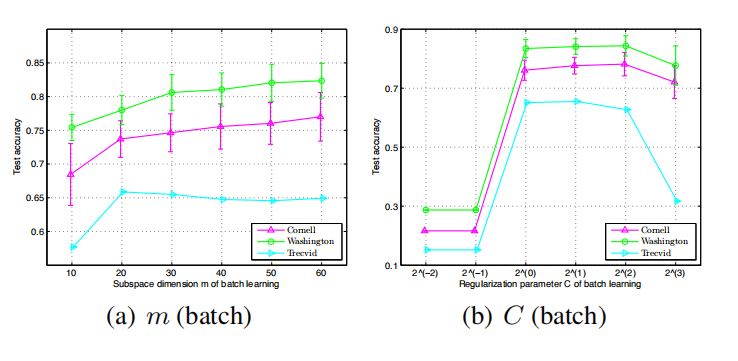
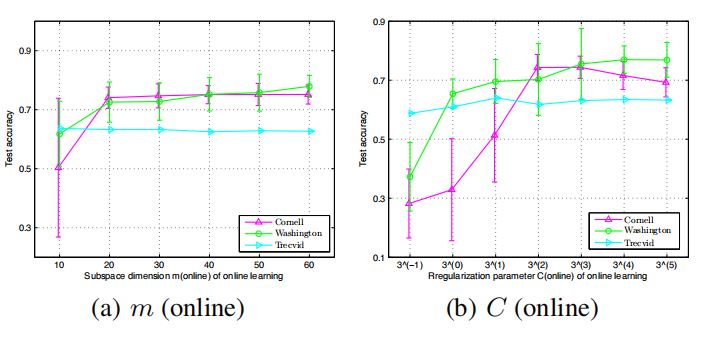
Last decades have witnessed a number of studies
devoted to multi-view learning algorithms, however, few efforts have been made to handle online multi-view learning scenarios. In this paper,
we propose an online Bayesian multi-view learning algorithm to learn predictive subspace with
max-margin principle. Specifically, we first de-
fine the latent margin loss for classification in the
subspace, and then cast the learning problem into
a variational Bayesian framework by exploiting
the pseudo-likelihood and data augmentation idea.
With the variational approximate posterior inferred
from the past samples, we can naturally combine
historical knowledge with new arrival data, in a
Bayesian Passive-Aggressive style. Experiments
on various classification tasks show that our model
have superior performance.
|
|
|
Zhao Zhang, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Hengshu Zhu, Zhiping Shi, Hui Xiong, Qing He: Relational Graph Neural Network with Hierarchical Attention for Knowledge Graph Completion. AAAI 2020.
-
The rapid proliferation of knowledge graphs (KGs) has
changed the paradigm for various AI-related applications.
Despite their large sizes, modern KGs are far from complete and comprehensive. This has motivated the research
in knowledge graph completion (KGC), which aims to infer missing values in incomplete knowledge triples. However,
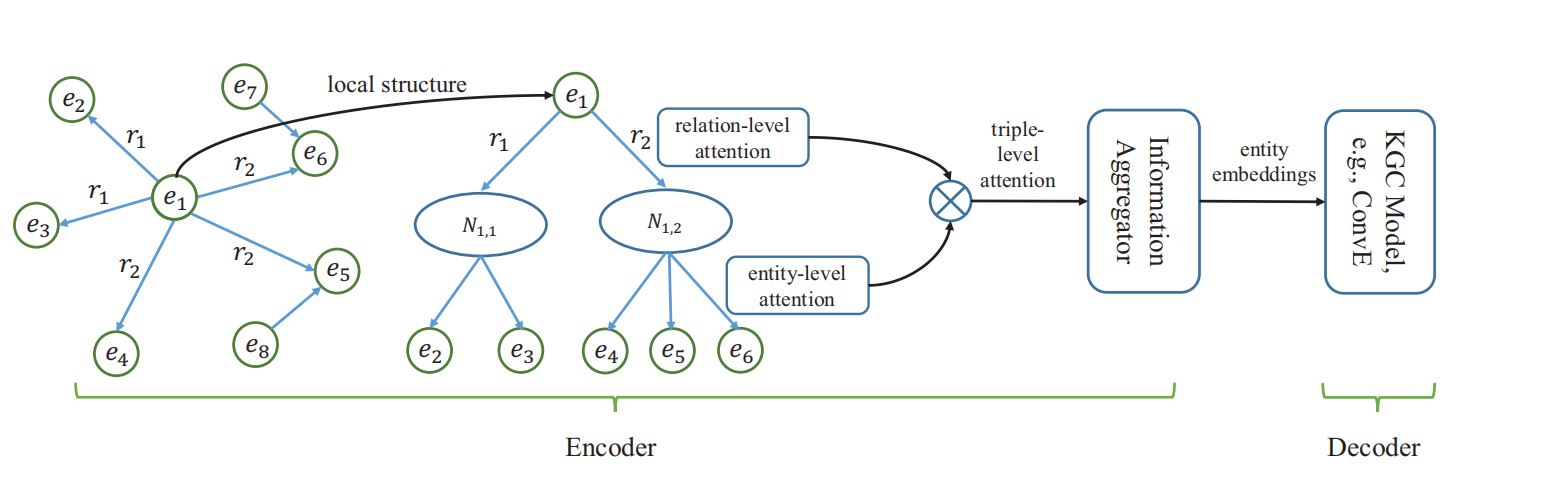
most existing KGC models treat the triples in KGs independently without leveraging the inherent and valuable information from the local neighborhood surrounding an entity. To
this end, we propose a Relational Graph neural network with
Hierarchical ATtention (RGHAT) for the KGC task. The proposed model is equipped with a two-level attention mechanism: (i) the first level is the relation-level attention, which is
inspired by the intuition that different relations have different
weights for indicating an entity; (ii) the second level is the
entity-level attention, which enables our model to highlight
the importance of different neighboring entities under the
same relation. The hierarchical attention mechanism makes
our model more effective to utilize the neighborhood information of an entity. Finally, we extensively validate the superiority of RGHAT against various state-of-the-art baselines.
|
|
Jingwu Chen, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Tianxin Wang, Leyu Lin, Feng Xia, Lihuan Du, Qing He: Follow the Title then Read the Article: Click-guide Network for Dwell Time Prediction. IEEE TKDE, 2019
-
In article recommendation, the amount of time user spends on viewing articles, dwell time, is an important metric to measure
the post-click engagement of user on content and has been widely used as a proxy to user satisfaction, complementing the click
feedback. Recently, the sequential pattern of impression-click-read has become one of the most popular type of article recommendation
service in real world, where users are presented with a list of titles at first, then get interested in one and click in for reading. Predicting
dwell time in such service is conditioned on the click, since the user reads the article only after he clicks the corresponding title. We argue
that conventional models for dwell time prediction, which mainly focus on the relevance between the content and the general preference
of user, are not well-designed for such service. There is a natural assumption in recommendation system that the click indicates user’s
getting attracted by the item. Therefore, in the pattern of impression-click-read, the user might get interested and curious on some other
concepts different from his general preference while reading, due to the attraction of the title. Conventional models tend to ignore the gap
between such temporary interest and the general preference of user in the reading behavior, which fails to use the pattern of impressionclick-read and the assumption of the click very well. In this work, we propose a framework, Click-guide Network (CGN) for dwell time
prediction, which makes good use of the sequential pattern and the assumption to model the ”guidance” of the click on user preference.
CGN is a joint learner for dwell time and click through rate (CTR). We introduce the CTR task as an auxiliary task to help us better learn
the preference of user and the representation of title. Besides, we propose the Guider to capture the user’s temporary interest raised by
the title. We collect the data from WeChat, a widely-used mobile app in China, for experiments. The results demonstrate the advantages
of CGN over several competitive baselines on dwell time prediction, while our case studies show how the Guider effectively capture the
temporary interest of user.
|
|
Xiao Zhang, Fuzhen Zhuang, Wenzhong Li, Haochao Ying, Hui Xiong, Sanglu Lu: Inferring Mood Instability via Smartphone Sensing: A Multi-View Learning Approach. ACM Multimedia 2019.
-
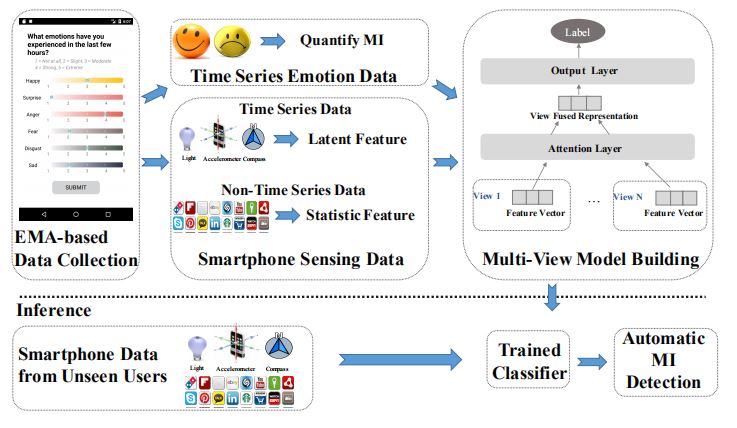
A high correlation between mood instability (MI), the rapid and constant fluctuation in mood, and mental health has been demonstrated.
However, conventional approaches to measure MI are limited owing to the high manpower and time cost required. In this paper, we
propose a smartphone-based MI detection that can automatically
and passively detect MI with minimal human involvement. The
proposed method trains a multi-view learning classification model
using features extracted from the smartphone sensing data of volunteers and their self-reported moods. The trained classifier is then
used to detect the MI of unseen users efficiently, thereby reducing
the human involvement and time cost significantly. Based on extensive experiments conducted with the dataset collected from 68
volunteers, we demonstrate that the proposed multi-view learning
model outperforms the baseline classifiers.
|
|
Jiejie Zhao, Bowen Du, Leilei Sun, Fuzhen Zhuang, Weifeng Lv, Hui Xiong: Multiple Relational Attention Network for Multi-task Learning. KDD 2019.
-
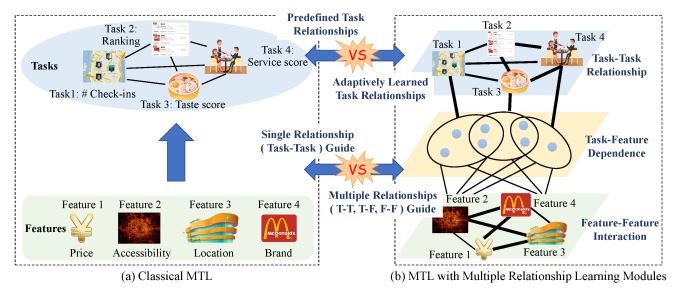
Multi-task learning is a successful machine learning framework
which improves the performance of prediction models by leveraging knowledge among tasks, e.g., the relationships between different tasks. Most of existing multi-task learning methods focus
on guiding learning process by predefined task relationships. In
fact, these methods have not fully exploited the associated relationships during the learning process. On the one hand, replacing
predefined task relationships by adaptively learned ones may result
in higher prediction accuracy as it can avoid the risk of misguiding caused by improperly predefined relationships. On the other
hand, apart from the task relationships, feature-task dependence
and feature-feature interactions could also be employed to guide the
learning process. Along this line, we propose a Multiple Relational
Attention Network (MRAN) framework for multi-task learning,
in which three types of relationships are considered. Correspondingly, MRAN consists of three attention-based relationship learning
modules: 1) a task-task relationship learning module which captures the relationships among tasks automatically and controls the
positive and negative knowledge transfer adaptively; 2) a featurefeature interaction learning module that handles the complicated
interactions among features; 3) a task-feature dependence learning
module, which can associate the related features with target tasks
separately. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed MARN,
experiments are conducted on two public datasets and a real-world
dataset crawled from a review hosting site. Experimental results
demonstrate the superiority of our method over both classical and
the state-of-the-art multi-task learning methods.
|
|
Fuzhen Zhuang , Xuebing Li , Xin Jin , Dapeng Zhang , Lirong Qiu , Qing He : Semantic Feature Learning for Heterogeneous Multitask Classification via Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. IEEE Trans, 2018.
-
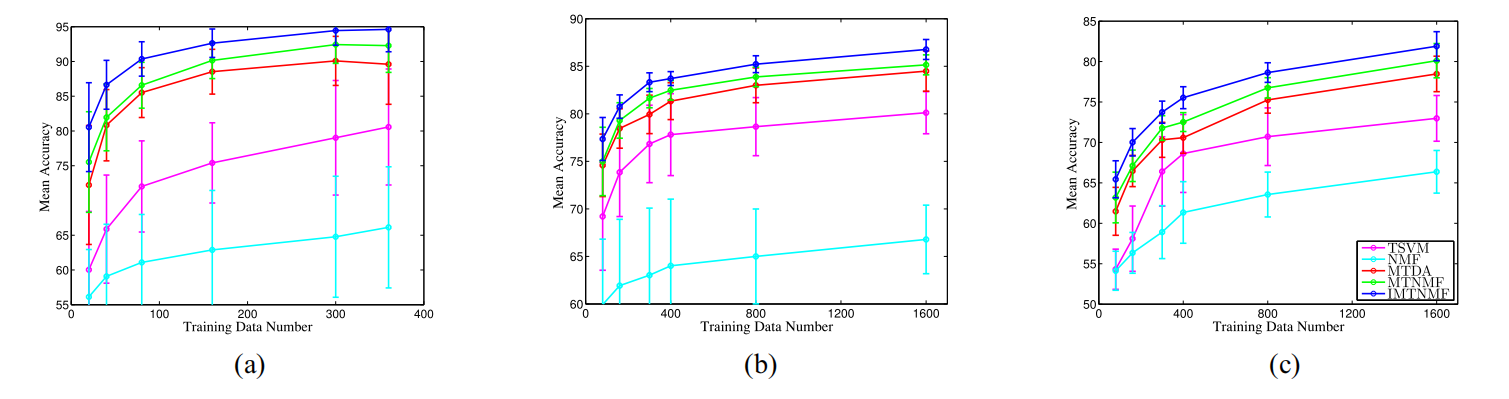
Multitask learning (MTL) aims to learn multiple
related tasks simultaneously instead of separately to improve
the generalization performance of each task. Most existing MTL
methods assumed that the multiple tasks to be learned have the
same feature representation. However, this assumption may not
hold for many real-world applications. In this paper, we study
the problem of MTL with heterogeneous features for each task.
To address this problem, we first construct an integrated graph
of a set of bipartite graphs to build a connection among different
tasks. We then propose a non-negative matrix factorization-based
multitask method (MTNMF) to learn a common semantic feature
space underlying different heterogeneous feature spaces of each
task. Moreover, an improved version of MTNMF (IMTNMF) is
proposed, in which we do not need to construct the correlation
matrix between input features and class labels, avoiding the information loss. Finally, based on the common semantic features and
original heterogeneous features, we model the heterogenous MTL
problem as a multitask multiview learning (MTMVL) problem.
In this way, a number of existing MTMVL methods can be
applied to solve the problem effectively. Extensive experiments
on three real-world problems demonstrate the effectiveness of
our proposed methods, and the improved version IMTNMF can
gain about 2% average accuracy improvement compared with
MTNMF.
|
|
Zhao Zhang , Fuzhen Zhuang* , Meng Qu , Fen Lin , Qing He : Knowledge Graph Embedding with Hierarchical Relation Structure. EMNLP 2018.
-
The rapid development of knowledge graphs
(KGs), such as Freebase and WordNet, has
changed the paradigm for AI-related applications. However, even though these KGs are
impressively large, most of them are suffering
from incompleteness, which leads to performance degradation of AI applications. Most
existing researches are focusing on knowledge graph embedding (KGE) models. Nevertheless, those models simply embed entities
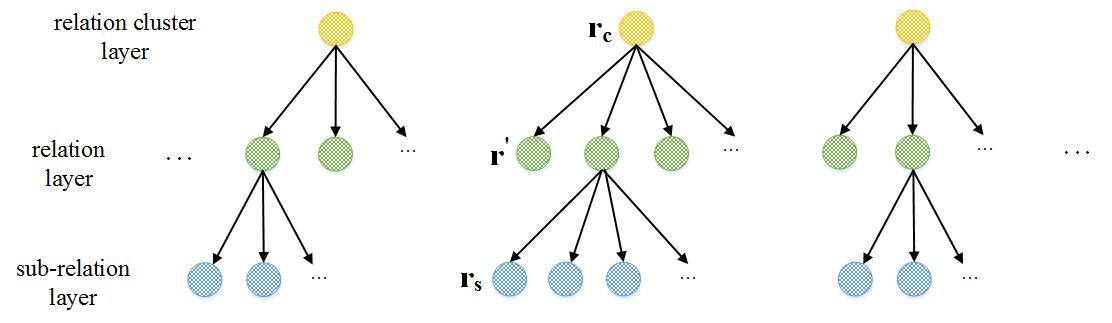
and relations into latent vectors without leveraging the rich information from the relation
structure. Indeed, relations in KGs conform
to a three-layer hierarchical relation structure
(HRS), i.e., semantically similar relations can
make up relation clusters and some relations
can be further split into several fine-grained
sub-relations. Relation clusters, relations and
sub-relations can fit in the top, the middle and
the bottom layer of three-layer HRS respectively. To this end, in this paper, we extend existing KGE models TransE, TransH and DistMult, to learn knowledge representations by
leveraging the information from the HRS. Particularly, our approach is capable to extend
other KGE models. Finally, the experiment results clearly validate the effectiveness of the
proposed approach against baselines.
|
|
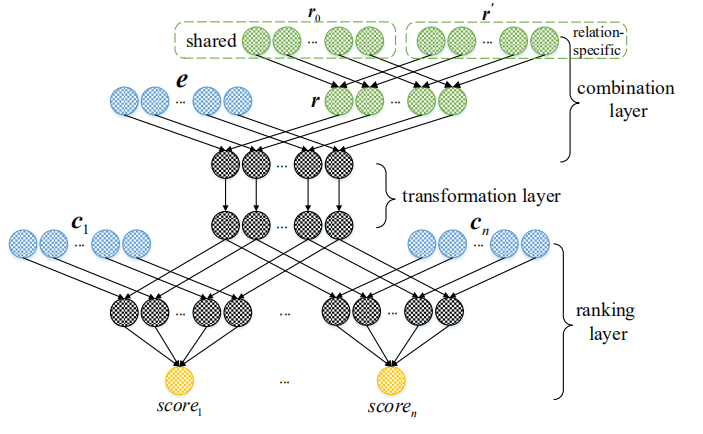
Zhao Zhang , Fuzhen Zhuang , Zheng-Yu Niu , Deqing Wang , Qing He : MultiE: Multi-Task Embedding for Knowledge Base Completion. CIKM 2018.
|
-
Completing knowledge bases (KBs) with missing facts is of great
importance, since most existing KBs are far from complete. To this
end, many knowledge base completion (KBC) methods have been
proposed. However, most existing methods embed each relation into
a vector separately, while ignoring the correlations among different
relations. Actually, in large-scale KBs, there always exist some
relations that are semantically related, and we believe this can help
to facilitate the knowledge sharing when learning the embedding
of related relations simultaneously. Along this line, we propose
a novel KBC model by Multi-Task Embedding, named MultiE. In
this model, semantically related relations are first clustered into
the same group, and then learning the embedding of each relation
can leverage the knowledge among different relations. Moreover,
we propose a three-layer network to predict the missing values
of incomplete knowledge triples. Finally, experiments on three
popular benchmarks FB15k, FB15k-237 and WN18 are conducted
to demonstrate the effectiveness of MultiE against some state-ofthe-art baseline competitors.
|
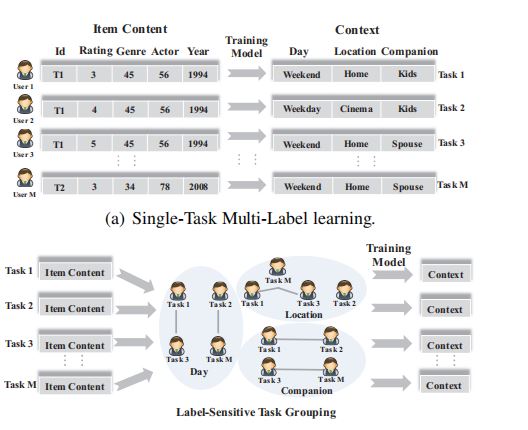
Xiao Zhang , Wenzhong Li , Vu Nguyen , Fuzhen Zhuang* , Hui Xiong , Sanglu Lu : Label-Sensitive Task Grouping by Bayesian Nonparametric Approach for Multi-Task Multi-Label Learning. IJCAI 2018.
|
-
Multi-label learning is widely applied in many realworld applications, such as image and gene annotation. While most of the existing multi-label
learning models focus on the single-task learning
problem, there are always some tasks that share
some commonalities, which can help each other to
improve the learning performances if the knowledge in the similar tasks can be smartly shared.
In this paper, we propose a LABel-sensitive TAsk
Grouping framework, named LABTAG, based on
Bayesian nonparametric approach for multi-task
multi-label classification. The proposed framework
explores the label correlations to capture featurelabel patterns, and clusters similar tasks into groups
with shared knowledge, which are learned jointly
to produce a strengthened multi-task multi-label
model. We evaluate the model performance on
three public multi-task multi-label data sets, and the
results show that LABTAG outperforms the compared baselines with a significant margin.
|
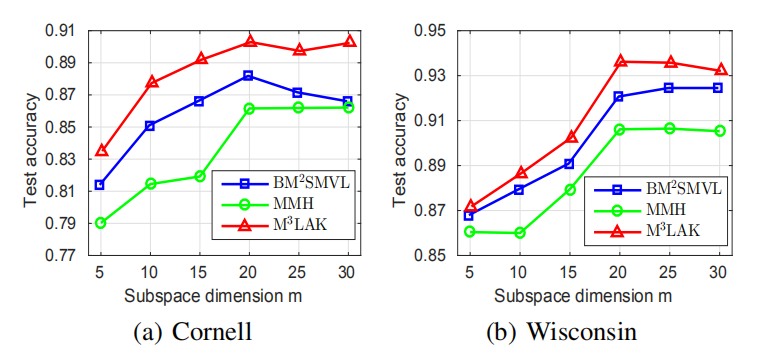
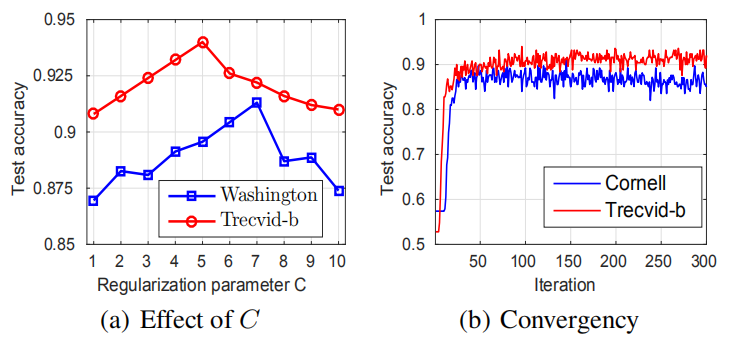
Jia He , Changying Du , Changde Du , Fuzhen Zhuang , Qing He , Guoping Long : Nonlinear Maximum Margin Multi-View Learning with Adaptive Kernel. IJCAI 2017.
-
Existing multi-view learning methods based on kernel function either require the user to select and
tune a single predefined kernel or have to compute
and store many Gram matrices to perform multiple
kernel learning. Apart from the huge consumption
of manpower, computation and memory resources,
most of these models seek point estimation of their
parameters, and are prone to overfitting to small training data. This paper presents an adaptive
kernel nonlinear max-margin multi-view learning
model under the Bayesian framework. Specifically, we regularize the posterior of an efficient multiview latent variable model by explicitly mapping
the latent representations extracted from multiple
data views to a random Fourier feature space where
max-margin classification constraints are imposed.
Assuming these random features are drawn from
Dirichlet process Gaussian mixtures, we can adaptively learn shift-invariant kernels from data according to Bochners theorem. For inference, we
employ the data augmentation idea for hinge loss,
and design an efficient gradient-based MCMC sampler in the augmented space. Having no need to
compute the Gram matrix, our algorithm scales linearly with the size of training set. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that our
method has superior performance.
|
|
|
Jia He , Changying Du , Fuzhen Zhuang , Xin Yin , Qing He , Guoping Long : Online Bayesian Max-Margin Subspace Multi-View Learning. IJCAI 2016.
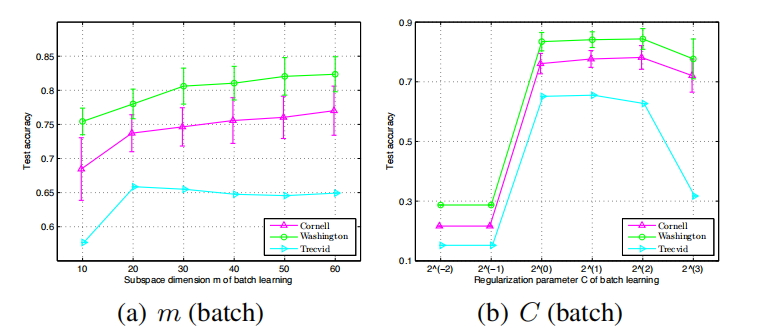
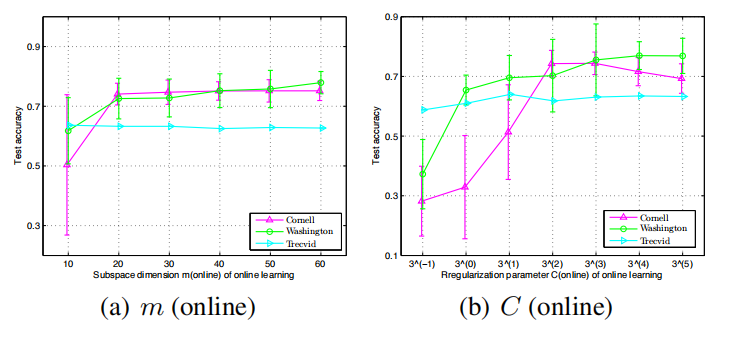
|
-
Last decades have witnessed a number of studies
devoted to multi-view learning algorithms, however, few efforts have been made to handle online multi-view learning scenarios. In this paper,
we propose an online Bayesian multi-view learning algorithm to learn predictive subspace with
max-margin principle. Specifically, we first de-
fine the latent margin loss for classification in the
subspace, and then cast the learning problem into
a variational Bayesian framework by exploiting
the pseudo-likelihood and data augmentation idea.
With the variational approximate posterior inferred
from the past samples, we can naturally combine
historical knowledge with new arrival data, in a
Bayesian Passive-Aggressive style. Experiments
on various classification tasks show that our model
have superior performance.
|
Fuzhen Zhuang, George Karypis, Xia Ning, Qing He, Zhongzhi Shi.: Multi-view Learning via Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis. Information Sciences,2012.
-
Multi-view learning arouses vast amount of interest in the past decades with numerous
real-world applications in web page analysis, bioinformatics, image processing and so
on. Unlike the most previous works following the idea of co-training, in this paper we propose a new generative model for Multi-view Learning via Probabilistic Latent Semantic
Analysis, called MVPLSA. In this model, we jointly model the co-occurrences of features
and documents from different views. Specifically, in the model there are two latent variables y for the latent topic and z for the document cluster, and three visible variables d
for the document, f for the feature, and v for the view label. The conditional probability
p(zjd), which is independent of v, is used as the bridge to share knowledge among multiple
views. Also, we have p(yjz, v) and p(fjy, v), which are dependent of v, to capture the specifical structures inside each view. Experiments are conducted on four real-world data sets to
demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our model.
|
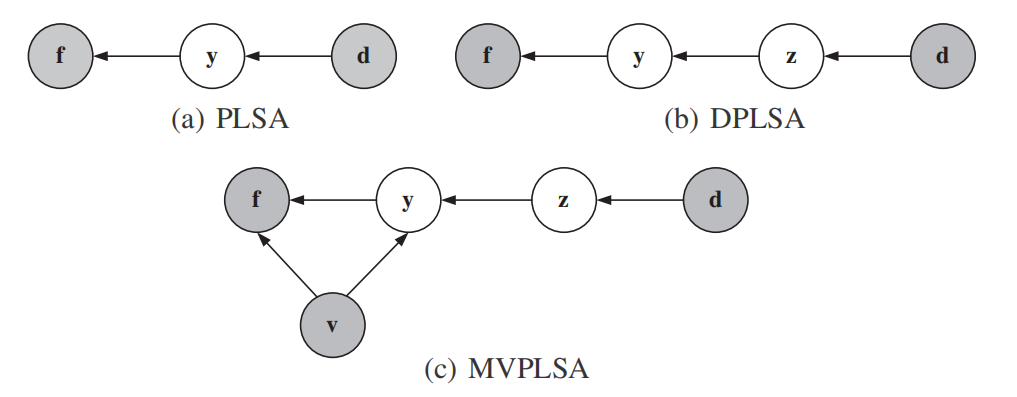
|
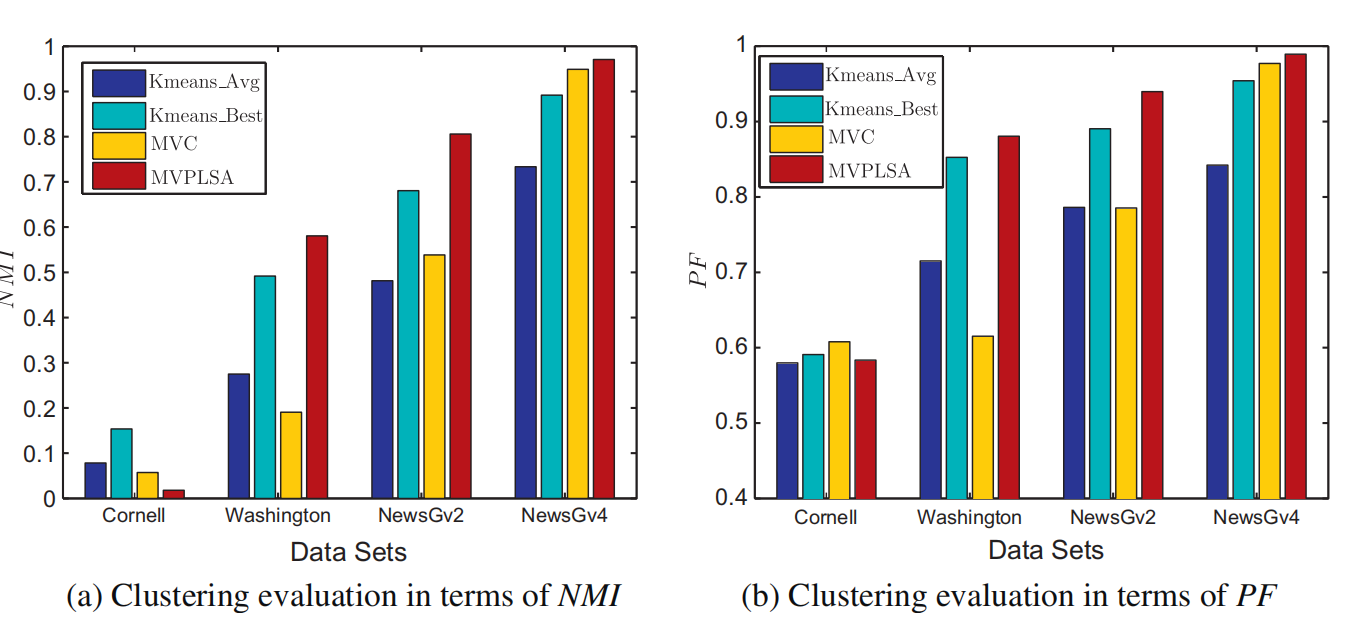
|
|















