Recommendation System
Yuanbo Xu, Yongjian Yang, En Wang, Fuzhen Zhuang, Hui Xiong.: Detect Professional Malicious User with Metric Learning in Recommender Systems. IEEE TKDE, 2020.
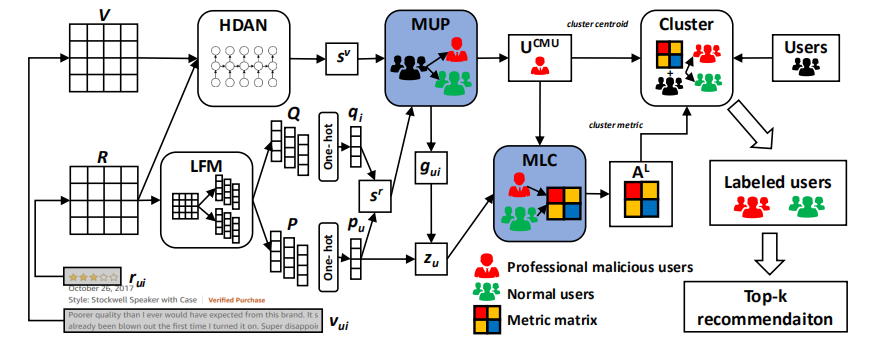
In e-commerce, online retailers are usually suffering from professional malicious users (PMUs), who utilize negative reviews
and low ratings to their consumed products on purpose to threaten the retailers for illegal profits. PMUs are difficult to be detected
because they utilize masking strategies to disguise themselves as normal users. Specifically, there are three challenges for PMU
detection: 1) professional malicious users do not conduct any abnormal or illegal interactions (they never concurrently leave too many
negative reviews and low ratings at the same time), and they conduct masking strategies to disguise themselves. Therefore,
conventional outlier detection methods are confused by their masking strategies. 2) the PMU detection model should take both ratings
and reviews into consideration, which makes PMU detection a multi-modal problem. 3) there are no datasets with labels for
professional malicious users in public, which makes PMU detection an unsupervised learning problem. To this end, we propose an
unsupervised multi-modal learning model: MMD, which employs Metric learning for professional Malicious users Detection with both
ratings and reviews. MMD first utilizes a modified RNN to project the informational review into a sentiment score, which jointly
considers the ratings and reviews. Then professional malicious user profiling (MUP) is proposed to catch the sentiment gap between
sentiment scores and ratings. MUP filters the users and builds a candidate PMU set. We apply a metric learning-based clustering to
learn a proper metric matrix for PMU detection. Finally, we can utilize this metric and labeled users to detect PMUs. Specifically, we
apply the attention mechanism in metric learning to improve the model’s performance. The extensive experiments in four datasets
demonstrate that our proposed method can solve this unsupervised detection problem. Moreover, the performance of the
state-of-the-art recommender models is enhanced by taking MMD as a preprocessing stage.
|
 |
Qingyu Guo, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Chuan Qin, Hengshu Zhu, Xing Xie, Hui Xiong, Qing He: A Survey on Knowledge Graph-Based Recommender Systems. IEEE TKDE, 2020.
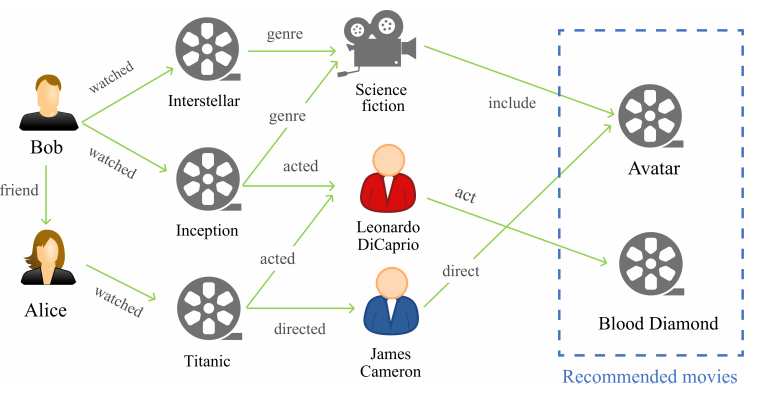 |
To solve the information explosion problem and enhance user experience in various online applications, recommender
systems have been developed to model users’ preferences. Although numerous efforts have been made toward more personalized
recommendations, recommender systems still suffer from several challenges, such as data sparsity and cold-start problems. In recent
years, generating recommendations with the knowledge graph as side information has attracted considerable interest. Such an
approach can not only alleviate the above mentioned issues for a more accurate recommendation, but also provide explanations for
recommended items. In this paper, we conduct a systematical survey of knowledge graph-based recommender systems. We collect
recently published papers in this field, and group them into three categories, i.e., embedding-based methods, connection-based
methods, and propagation-based methods. Also, we further subdivide each category according to the characteristics of these
approaches. Moreover, we investigate the proposed algorithms by focusing on how the papers utilize the knowledge graph for accurate
and explainable recommendation. Finally, we propose several potential research directions in this field.Experimental results on both industrial (fraud detection from real e-commerce platform) and public (movie rating) datasets clearly demonstrate that our model achieves significantly better performance compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
|
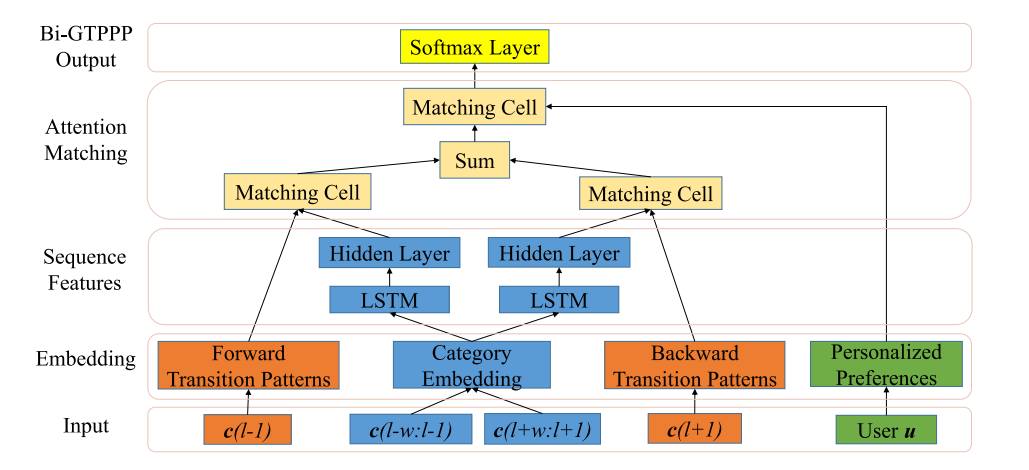
Dongbo Xi, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Yanchi Liu, Hengshu Zhu, Pengpeng Zhao, Chang Tan, Qing He: Exploiting Bi-directional Global Transition Patterns and Personal Preferences for Missing POI Category Identification. Neural Networks, 2020.
Recent years have witnessed the increasing popularity of Location-based Social Network (LBSN)
services, which provides unparalleled opportunities to build personalized Point-of-Interest (POI)
recommender systems. Existing POI recommendation and location prediction tasks utilize past information
for future recommendation or prediction from a single direction perspective, while the
missing POI category identification task needs to utilize the check-in information both before and
after the missing category. Therefore, a long-standing challenge is how to effectively identify the
missing POI categories at any time in the real-world check-in data of mobile users. To this end, in
this paper, we propose a novel neural network approach to identify the missing POI categories by
integrating both bi-directional global non-personal transition patterns and personal preferences of
users. Specifically, we delicately design an attention matching cell to model how well the check-in
category information matches their non-personal transition patterns and personal preferences. Finally,
we evaluate our model on two real-world datasets, which clearly validate its effectiveness compared
with the state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, our model can be naturally extended to address next
POI category recommendation and prediction tasks with competitive performance.
|
|
Pengpeng Zhao, Anjing Luo, Yanchi Liu, Jiajie Xu, Zhixu Li, Fuzhen Zhuang, Victor S. Sheng, Xiaofang Zhou: Where to Go Next: A Spatio-Temporal Gated Network for Next POI Recommendation. IEEE TKDE, 2020.
 |
—Next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation which is of great value to both users and POI holders is a challenging task
since complex sequential patterns and rich contexts are contained in extremely sparse user check-in data. Recently proposed
embedding techniques have shown promising results in alleviating the data sparsity issue by modeling context information, and
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) has been proved effective in the sequential prediction. However, existing next POI recommendation
approaches train the embedding and network model separately, which cannot fully leverage rich contexts. In this paper, we propose a
novel unified neural network framework, named NeuNext, which leverages POI context prediction to assist next POI recommendation
by joint learning. Specifically, the Spatio-Temporal Gated Network (STGN) is proposed to model personalized sequential patterns for
users’ long and short term preferences in the next POI recommendation. In the POI context prediction, rich contexts on POI sides are
used to construct graph, and enforce the smoothness among neighboring POIs. Finally, we jointly train the POI context prediction and
the next POI recommendation to fully leverage labeled and unlabeled data. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that
our method outperforms other approaches for next POI recommendation in terms of Accuracy and MAP.
|
Yuanbo Xu, Yongjian Yang, En Wang, Jiayu Han, Fuzhen Zhuang, Zhiwen Yu, Hui Xiong: Neural Serendipity Recommendation: Exploring the Balance between Accuracy and Novelty with sparse Explicit Feedback. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2020.
-
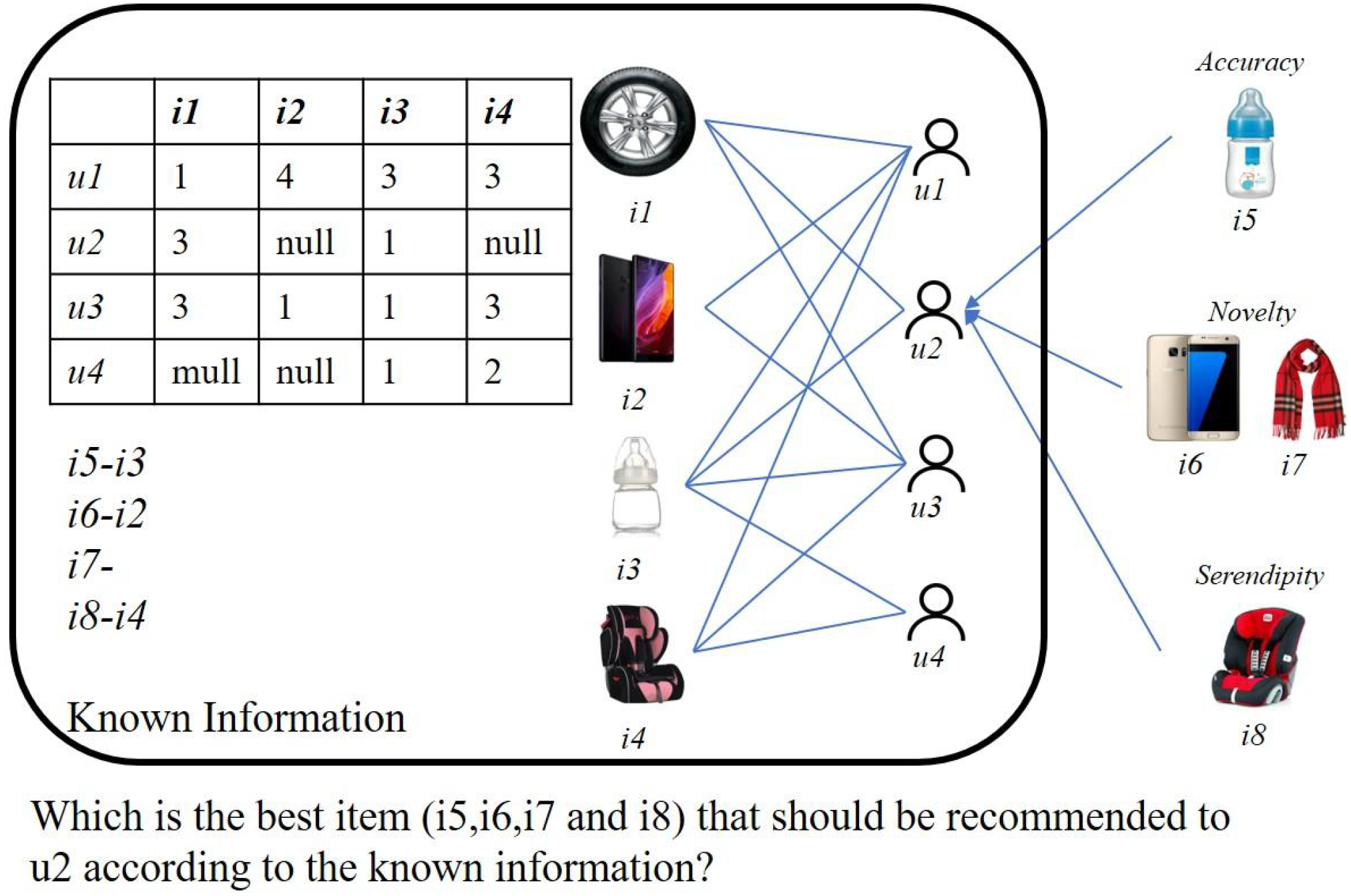
Recommender systems have been playing an important role in providing personalized information to users.
However, there is always a trade-off between accuracy and novelty in recommender systems. Usually, many
users are suffering from redundant or inaccurate recommendation results. To this end, in this article, we put
efforts into exploring the hidden knowledge of observed ratings to alleviate this recommendation dilemma.
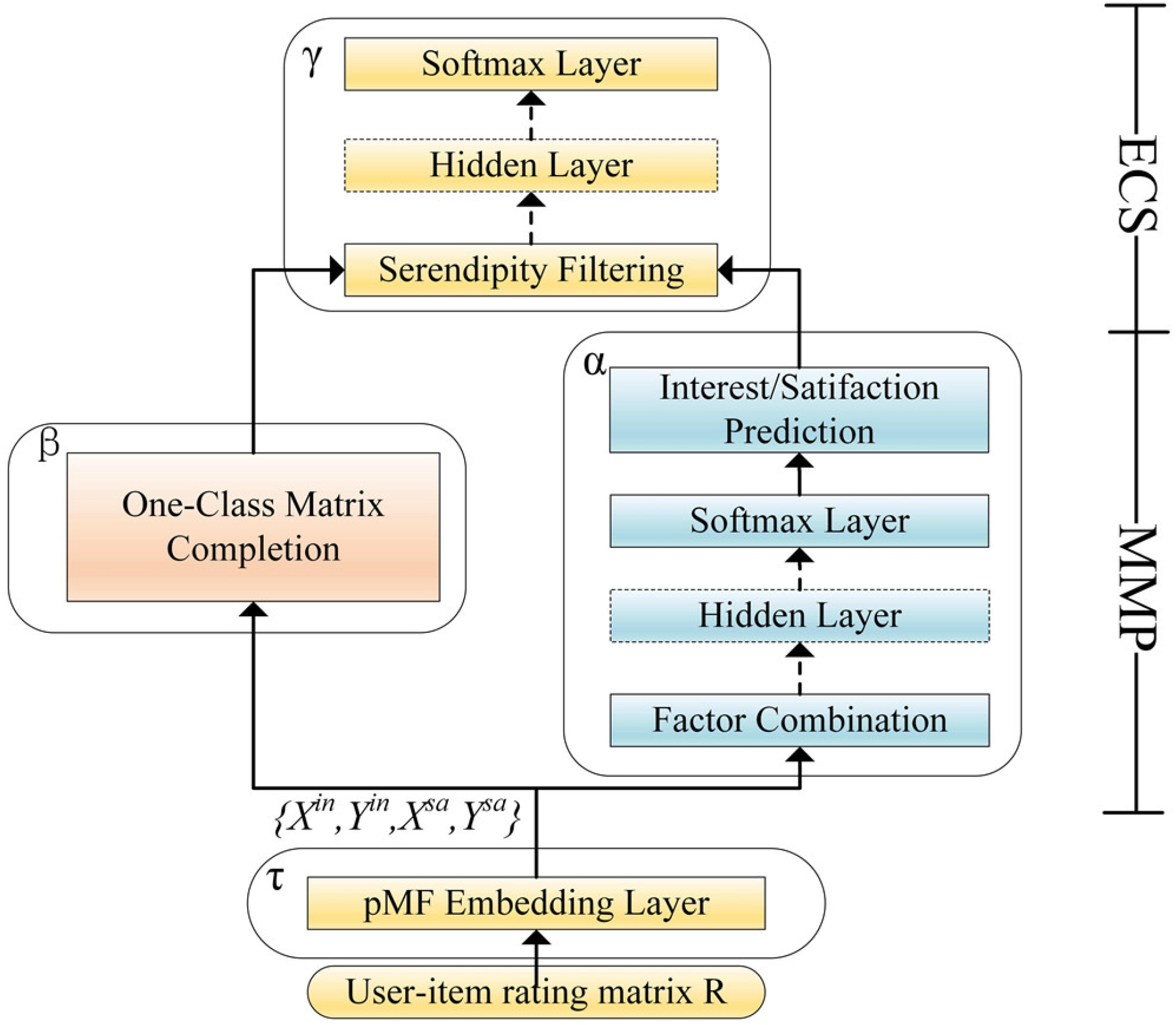
Specifically, we utilize some basic concepts to define a concept, Serendipity, which is characterized by highsatisfaction and low-initial-interest. Based on this concept, we propose a two-phase recommendation problem which aims to strike a balance between accuracy and novelty achieved by serendipity prediction and
personalized recommendation. Along this line, a Neural Serendipity Recommendation (NSR) method is first
developed by combining Muti-Layer Percetron and Matrix Factorization for serendipity prediction. Then, a
weighted candidate filtering method is designed for personalized recommendation. Finally, extensive experiments on real-world data demonstrate that NSR can achieve a superior serendipity by a 12% improvement
in average while maintaining stable accuracy compared with state-of-the-art methods.
|
 |
 |
Jiayu Han, Lei Zheng, Yuanbo Xu, Bangzuo Zhang, Fuzhen Zhuang, Philip Yu, Wanli Zuo: Adaptive Deep Modeling of Users and Items Using Side Information for Recommendation. IEEE Trans, 2020.
-
In the existing recommender systems, matrix factorization (MF) is widely applied to model user preferences and item
features by mapping the user-item ratings into a low-dimension
latent vector space. However, MF has ignored the individual
diversity where the user’s preference for different unrated items
is usually different. A fixed representation of user preference
factor extracted by MF cannot model the individual diversity
well, which leads to a repeated and inaccurate recommendation.
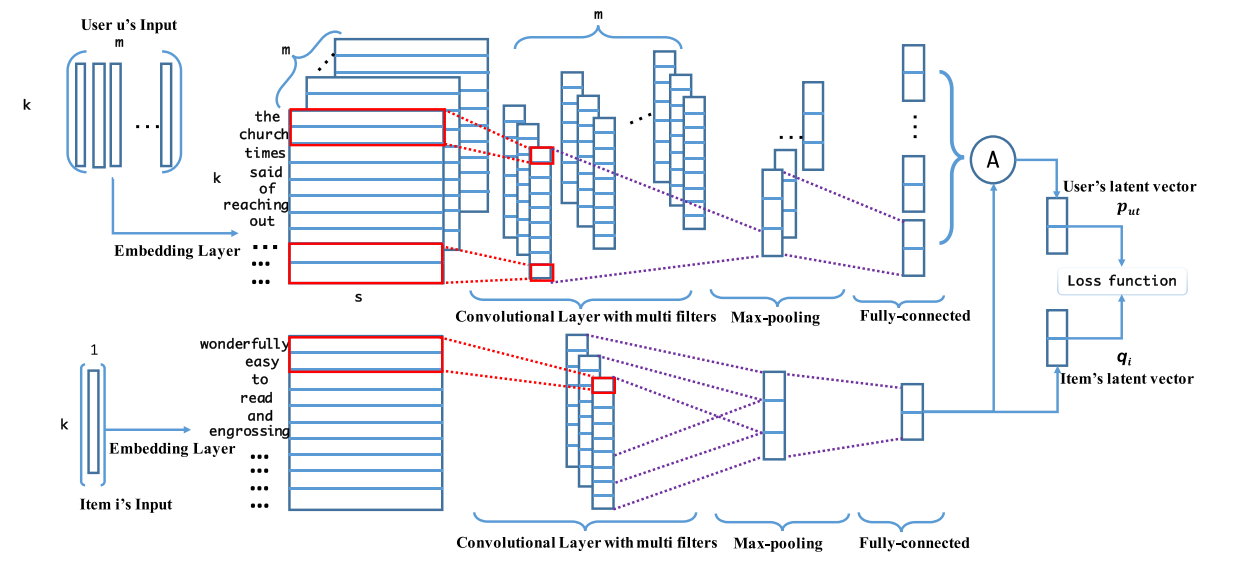
To this end, we propose a novel latent factor model called
adaptive deep latent factor model (ADLFM), which learns the
preference factor of users adaptively in accordance with the
specific items under consideration. We propose a novel user
representation method that is derived from their rated item
descriptions instead of original user-item ratings. Based on this,
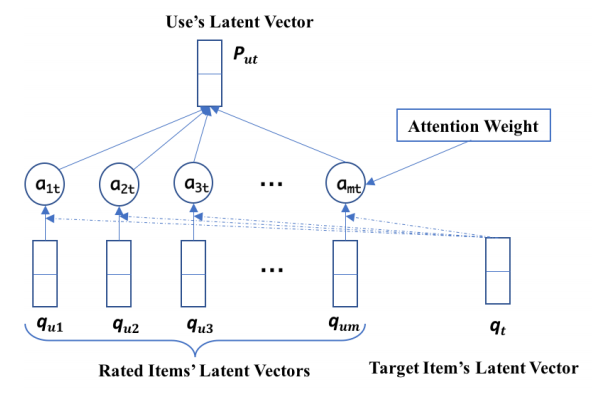
we further propose a deep neural networks framework with an
attention factor to learn the adaptive representations of users.
Extensive experiments on Amazon data sets demonstrate that
ADLFM outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines greatly. Also,
further experiments show that the attention factor indeed makes
a great contribution to our method.
|
 |
 |
Anjing Luo, Pengpeng Zhao, Yanchi Liu, Fuzhen Zhuang, Deqing Wang, Jiajie Xu, Junhua Fang and Victor Sheng: Collaborative Self-Attention Network for Session-based Recommendation. IJCAI 2020.
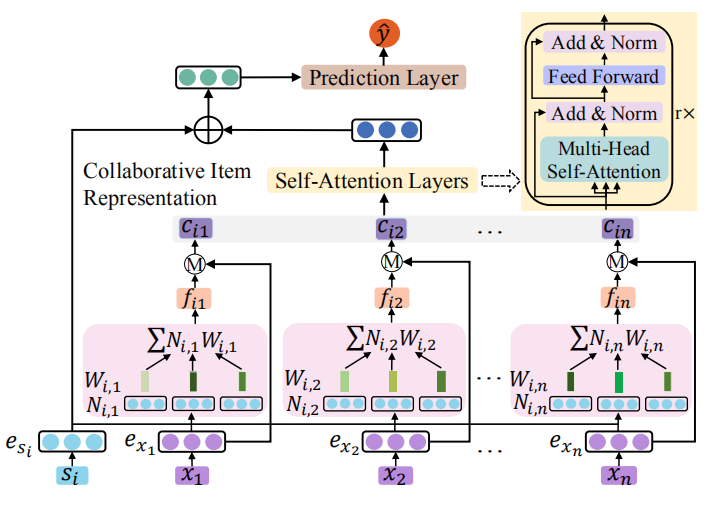 |
Session-based recommendation becomes a research hotspot for its ability to make recommendations for anonymous users. However, existing
session-based methods have the following limitations: (1) They either lack the capability to learn
complex dependencies or focus mostly on the current session without explicitly considering collaborative information. (2) They assume that the representation of an item is static and fixed for all users at each time step. We argue that even the
same item can be represented differently for different users at the same time step. To this end, we propose a novel solution, Collaborative Self-Attention
Network (CoSAN) for session-based recommendation, to learn the session representation and predict the intent of the current session by investigating
neighborhood sessions. Specially, we first devise
a collaborative item representation by aggregating
the embedding of neighborhood sessions retrieved
according to each item in the current session. Then,
we apply self-attention to learn long-range dependencies between collaborative items and generate
collaborative session representation. Finally, each
session is represented by concatenating the collaborative session representation and the embedding
of the current session. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets show that CoSAN constantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
|
Dongbo Xi, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Bowen Song, Yongchun Zhu, Shuai Chen, Dan Hong, Tao Chen, Xi Gu, and Qing He: Neural Hierarchical Factorization Machines for User’s Event Sequence Analysis. SIGIR 2020.
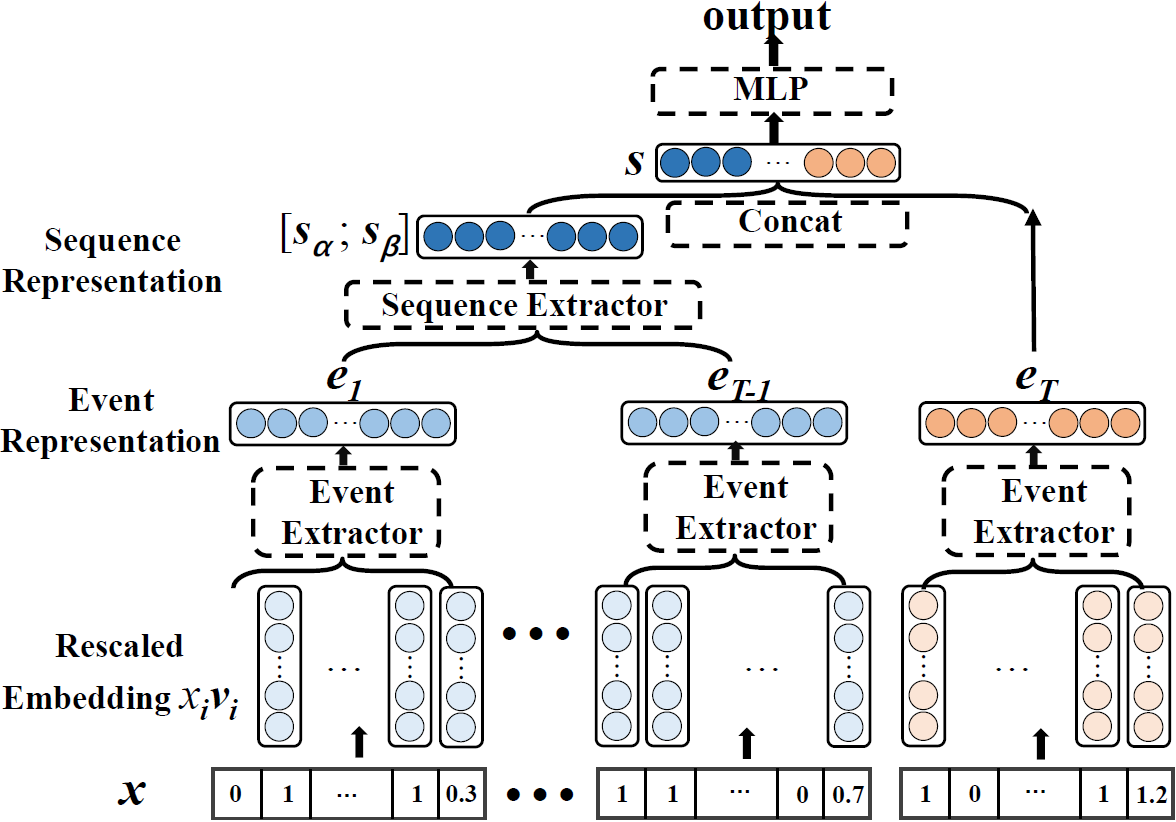 |
Many prediction tasks of real-world applications need to model multi-order feature interactions in user's event sequence for excellent performance. However, in industry and academia, existing popular solutions usually suffer two key issues: 1) only focusing on feature interactions and failing to capture the event sequence influence; 2) only focusing on event sequence information, but ignoring internal feature relations of each event, thus failing to extract a better event representation.
In this paper, we consider a two-level structure for capturing the hierarchical information over user's event sequence: 1) learning effective feature interactions based event representation; 2) modeling the sequence representation of user's historical events.
Experimental results on both industrial (fraud detection from real e-commerce platform) and public (movie rating) datasets clearly demonstrate that our model achieves significantly better performance compared with state-of-the-art baselines.
|
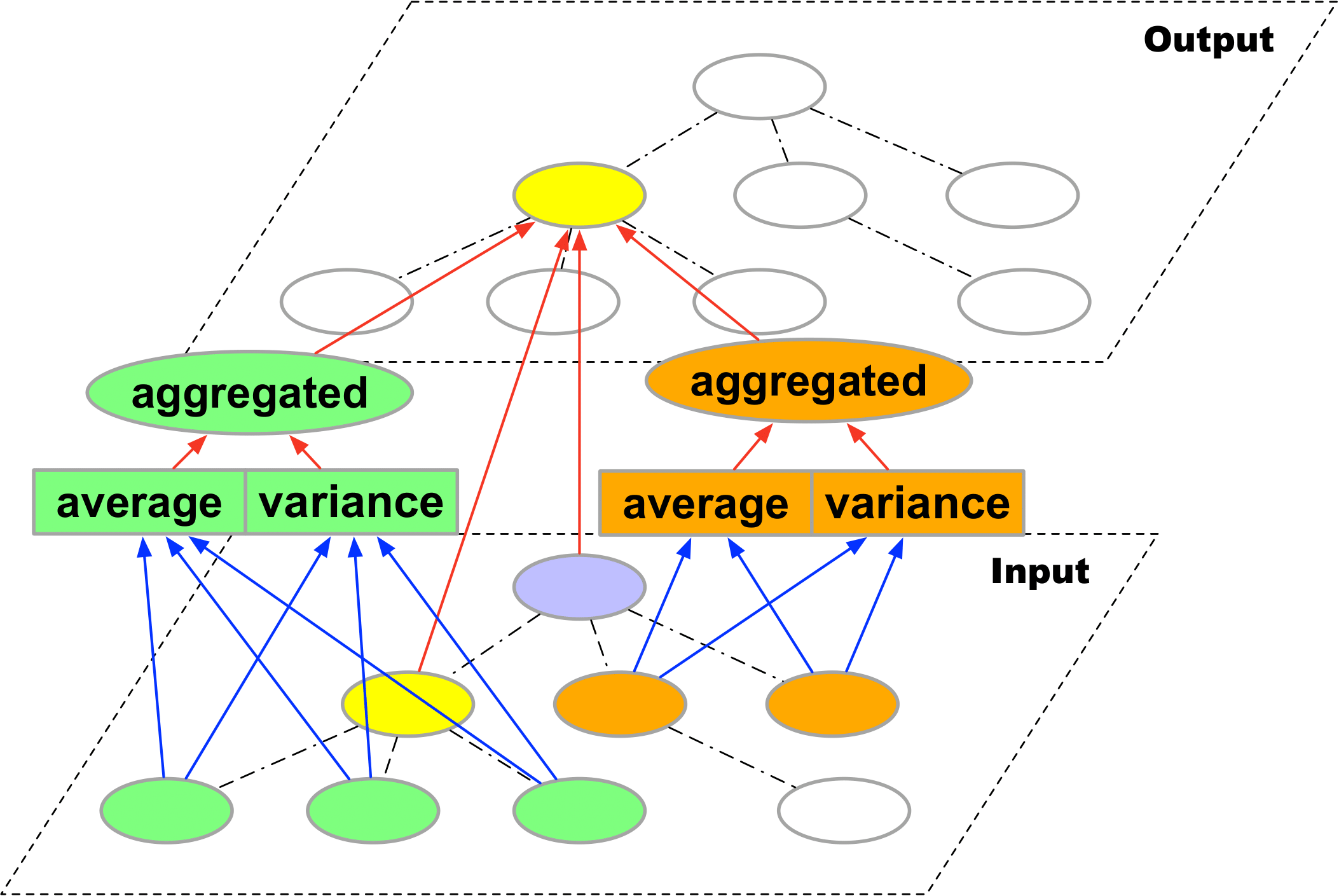
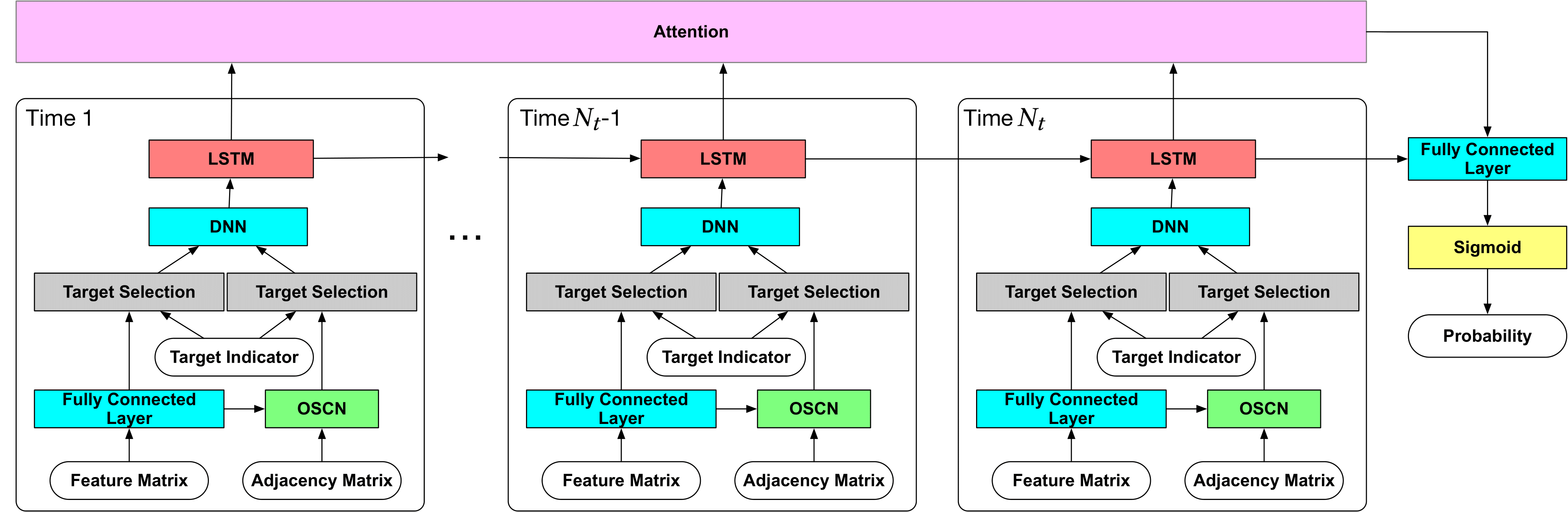
Ying Sun, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Hengshu Zhu*, Xin Song, Qing He, and Hui Xiong: The Impact of Person-Organization Fit on Talent Management: A Structure-Aware Convolutional Neural Network Approach. KDD 2019.
-
Person-Organization fit (P-O fit) refers to the compatibility between employees and their organizations. The study of P-O fit is important for enhancing proactive talent management.While considerable efforts have been made in this direction, it still lacks a quantitative and holistic way for measuring P-O fit and its impact on talent management. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel data-driven neural network approach for dynamically modeling the compatibility in P-O fit and its meaningful relationships with two critical issues in talent management, namely talent turnover and job performance.
Specifically, inspired by the practical management scenarios, we first creatively design an Organizational Structure-aware Convolutional Neural Network (OSCN) for hierarchically extracting organization-aware compatibility features for measuring P-O fit. Then, to capture the dynamic nature of P-O fit and its consequent impact, we further exploit an adapted Recurrent Neural Network with attention mechanism to model the temporal information of P-O fit.
We evaluate our approach with a number of state-of-the-art baseline methods on real-world talent data. Experimental results clearly demonstrate the effectiveness in terms of turnover prediction and job performance prediction, as well as some interesting indicators of talent management through the visualization of network layers. Moreover, our study reveals some management insights for enhancing proactive talent management. For instance, the results show that superiors usually have a great influence on the turnover intention of their subordinates.
|
 |
 |
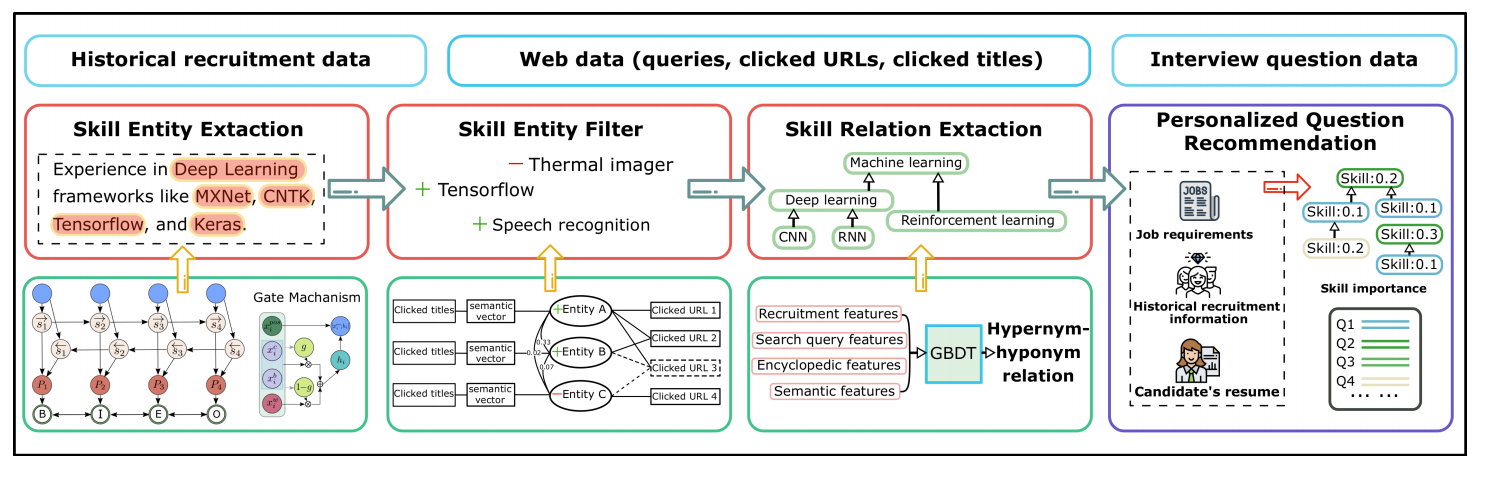
Chuan Qin, Hengshu Zhu, Chen Zhu, Tong Xu, Fuzhen Zhuang, Chao Ma, Jingshuai Zhang, Hui Xiong: DuerQuiz: A Personalized Question Recommender System for Intelligent Job Interview. KDD 2019.
-
In talent recruitment, the job interview aims at selecting the right
candidates for the right jobs through assessing their skills and
experiences in relation to the job positions. While tremendous
efforts have been made in improving job interviews, a long-standing
challenge is how to design appropriate interview questions for
comprehensively assessing the competencies that may be deemed
relevant and representative for person-job fit. To this end, in this
research, we focus on the development of a personalized question
recommender system, namely DuerQuiz, for enhancing the job
interview assessment. DuerQuiz is a fully deployed system, in which
a knowledge graph of job skills, Skill-Graph, has been built for
comprehensively modeling the relevant competencies that should
be assessed in the job interview. Specifically, we first develop a
novel skill entity extraction approach based on a bidirectional Long
Short-Term Memory (LSTM) with a Conditional Random Field (CRF)
layer (LSTM-CRF) neural network enhanced with adapted gate
mechanism. In particular, to improve the reliability of extracted
skill entities, we design a label propagation method based on more
than 10 billion click-through data from the large-scale Baidu query
logs. Furthermore, we discover the hypernym-hyponym relations
between skill entities and construct the Skill-Graph by leveraging
the classifier trained with extensive contextual features. Finally, we
design a personalized question recommendation algorithm based
on the Skill-Graph for improving the efficiency and effectiveness
of job interview assessment. Extensive experiments on real-world
recruitment data clearly validate the effectiveness of DuerQuiz,
which had been deployed for generating written exercises in the
2018 Baidu campus recruitment event and received remarkable
performances in terms of efficiency and effectiveness for selecting
outstanding talents compared with a traditional non-personalized
human-only assessment approach.
|
 |
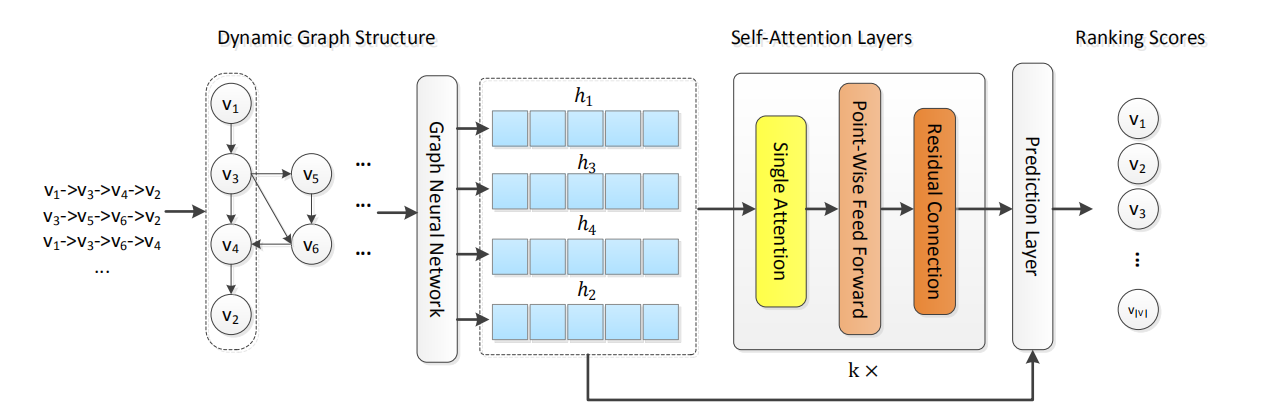
Chengfeng Xu, Pengpeng Zhao, Yanchi Liu, Victor S. Sheng, Jiajie Xu, Fuzhen Zhuang, Junhua Fang, Xiaofang Zhou: Graph Contextualized Self-Attention Network for Session-based Recommendation. IJCAI 2019.
Session-based recommendation, which aims to predict the user’s immediate next action based on
anonymous sessions, is a key task in many online
services (e.g., e-commerce, media streaming). Recently, Self-Attention Network (SAN) has achieved
significant success in various sequence modeling
tasks without using either recurrent or convolutional network. However, SAN lacks local dependencies that exist over adjacent items and limits its capacity for learning contextualized representations of items in sequences. In this paper, we propose a graph contextualized self-attention model
(GC-SAN), which utilizes both graph neural network and self-attention mechanism, for sessionbased recommendation. In GC-SAN, we dynamically construct a graph structure for session sequences and capture rich local dependencies via graph neural network (GNN). Then each session learns long-range dependencies by applying
the self-attention mechanism. Finally, each session
is represented as a linear combination of the global
preference and the current interest of that session.
Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets show that GC-SAN outperforms state-of-the-art
methods consistently.
|
 |
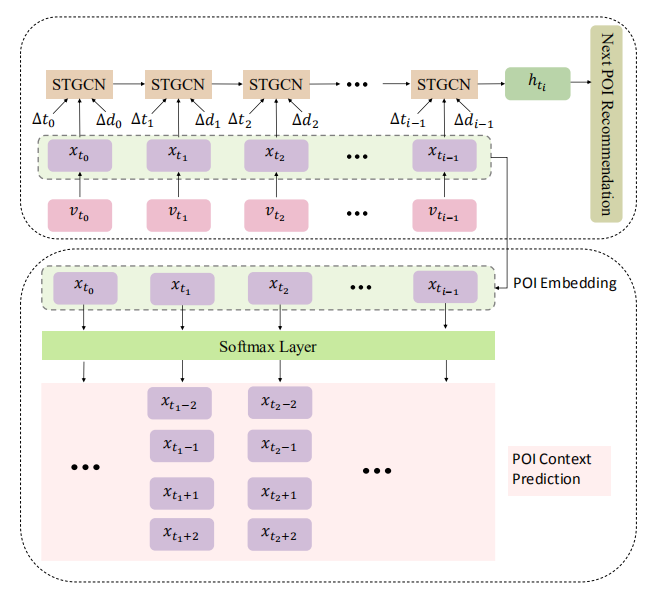
Pengpeng Zhao, Haifeng Zhu, Yanchi Liu, Jiajie Xu, Zhixu Li, Fuzhen Zhuang, Victor S. Sheng, Xiaofang Zhou: Where to Go Next: A Spatio-Temporal Gated Network for Next POI Recommendation. AAAI 2019.
 |
—Next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation which is of great value to both users and POI holders is a challenging task
since complex sequential patterns and rich contexts are contained in extremely sparse user check-in data. Recently proposed
embedding techniques have shown promising results in alleviating the data sparsity issue by modeling context information, and
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) has been proved effective in the sequential prediction. However, existing next POI recommendation
approaches train the embedding and network model separately, which cannot fully leverage rich contexts. In this paper, we propose a
novel unified neural network framework, named NeuNext, which leverages POI context prediction to assist next POI recommendation
by joint learning. Specifically, the Spatio-Temporal Gated Network (STGN) is proposed to model personalized sequential patterns for
users’ long and short term preferences in the next POI recommendation. In the POI context prediction, rich contexts on POI sides are
used to construct graph, and enforce the smoothness among neighboring POIs. Finally, we jointly train the POI context prediction and
the next POI recommendation to fully leverage labeled and unlabeled data. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that
our method outperforms other approaches for next POI recommendation in terms of Accuracy and MAP.
|
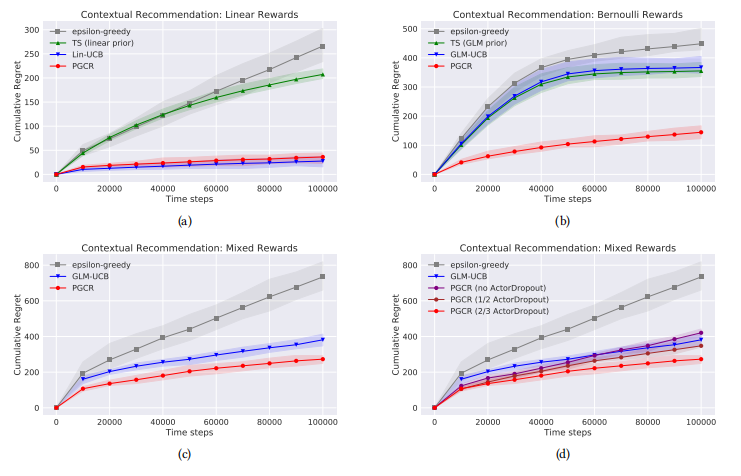
Feiyang Pan, Qingpeng Cai, Pingzhong Tang, Fuzhen Zhuang, Qing He: Policy Gradients for Contextual Recommendations. WWW 2019.
Decision making is a challenging task in online recommender systems. The decision maker often needs to choose a contextual item
at each step from a set of candidates. Contextual bandit algorithms
have been successfully deployed to such applications, for the tradeoff between exploration and exploitation and the state-of-art performance on minimizing online costs. However, the applicability of
existing contextual bandit methods is limited by the over-simplified
assumptions of the problem, such as assuming a simple form of the
reward function or assuming a static environment where the states
are not affected by previous actions.
In this work, we put forward Policy Gradients for Contextual
Recommendations (PGCR) to solve the problem without those unrealistic assumptions. It optimizes over a restricted class of policies
where the marginal probability of choosing an item (in expectation
of other items) has a simple closed form, and the gradient of the
expected return over the policy in this class is in a succinct form.
Moreover, PGCR leverages two useful heuristic techniques called
Time-Dependent Greed and Actor-Dropout. The former ensures
PGCR to be empirically greedy in the limit, and the latter addresses
the trade-off between exploration and exploitation by using the
policy network with Dropout as a Bayesian approximation.
PGCR can solve the standard contextual bandits as well as its
Markov Decision Process generalization. Therefore it can be applied
to a wide range of realistic settings of recommendations, such as
personalized advertising. We evaluate PGCR on toy datasets as well
as a real-world dataset of personalized music recommendations.
Experiments show that PGCR enables fast convergence and low
regret, and outperforms both classic contextual-bandits and vanilla
policy gradient methods.
|
 |
Dongbo Xi, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Yanchi Liu, Jingjing Gu, Hui Xiong, Qing He: Modelling of Bi-directional Spatio-Temporal Dependence and Users’ Dynamic Preferences for Missing POI Check-in Identification. AAAI 2019.
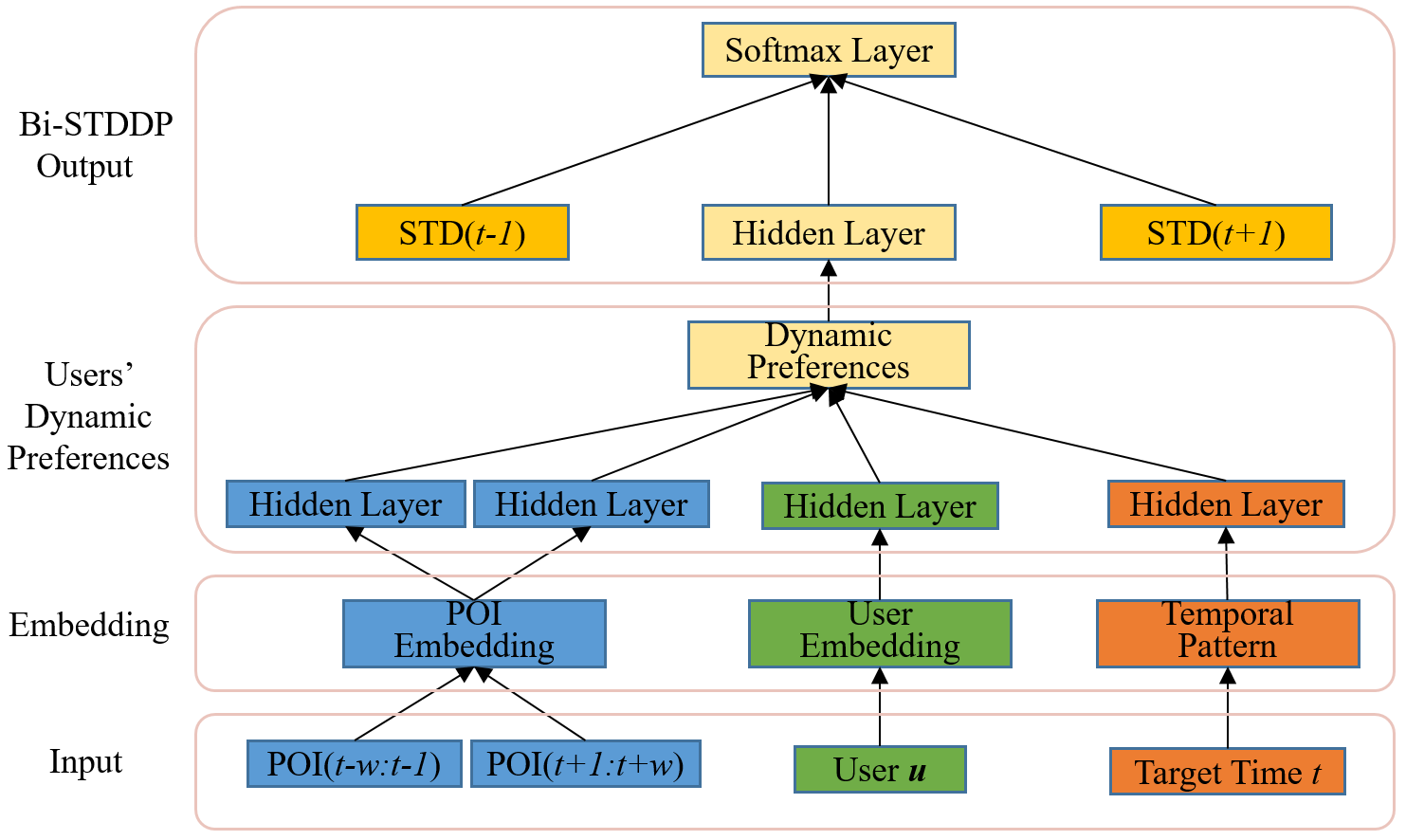 |
Human mobility data accumulated from Point-of-Interest (POI) check-ins provides great opportunity for user behavior understanding. However, data quality issues (e.g., geolocation information missing, unreal check-ins, data sparsity) in real-life mobility data limit the effectiveness of existing POI-oriented studies, e.g., POI recommendation and location prediction, when applied to real applications.
To this end, in this paper, we develop a model, named Bi-STDDP, which can integrate bi-directional spatio-temporal dependence and users’ dynamic preferences, to identify the missing POI check-in where a user has visited at a specific time. Specifically, we first utilize bi-directional global spatial and local temporal information of POIs to capture the complex dependence relationships. Then, target temporal pattern in combination with user and POI information are fed into a multi-layer network to capture users’ dynamic preferences. Moreover, the dynamic preferences are transformed into the same space as the dependence relationships to form the final model.
Finally, the proposed model is evaluated on three large-scale real-world datasets and the results demonstrate significant improvements of our model compared with state-of-the-art methods. Also, it is worth noting that the proposed model can be naturally extended to address POI recommendation and location prediction tasks with competitive performances.
|
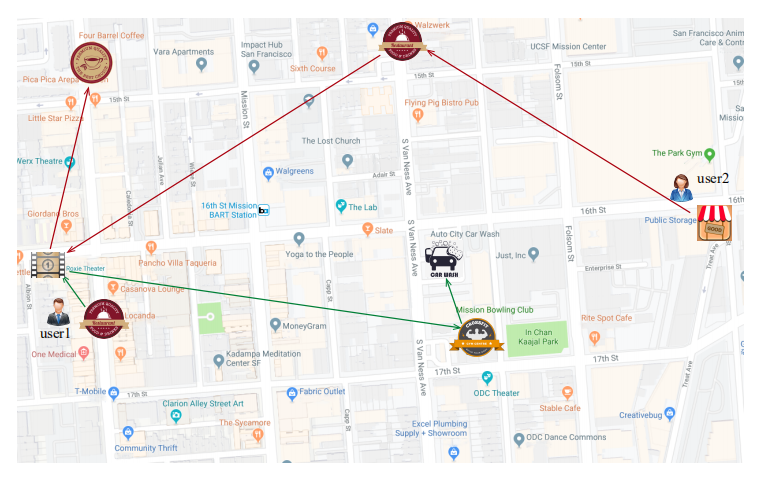
Ying Sun, Hengshu Zhu*, Fuzhen Zhuang*, Jingjing Gu, Qing He:Exploring the Urban Region-of-Interest through the Analysis of Online Map Search Queries. KDD 2018.
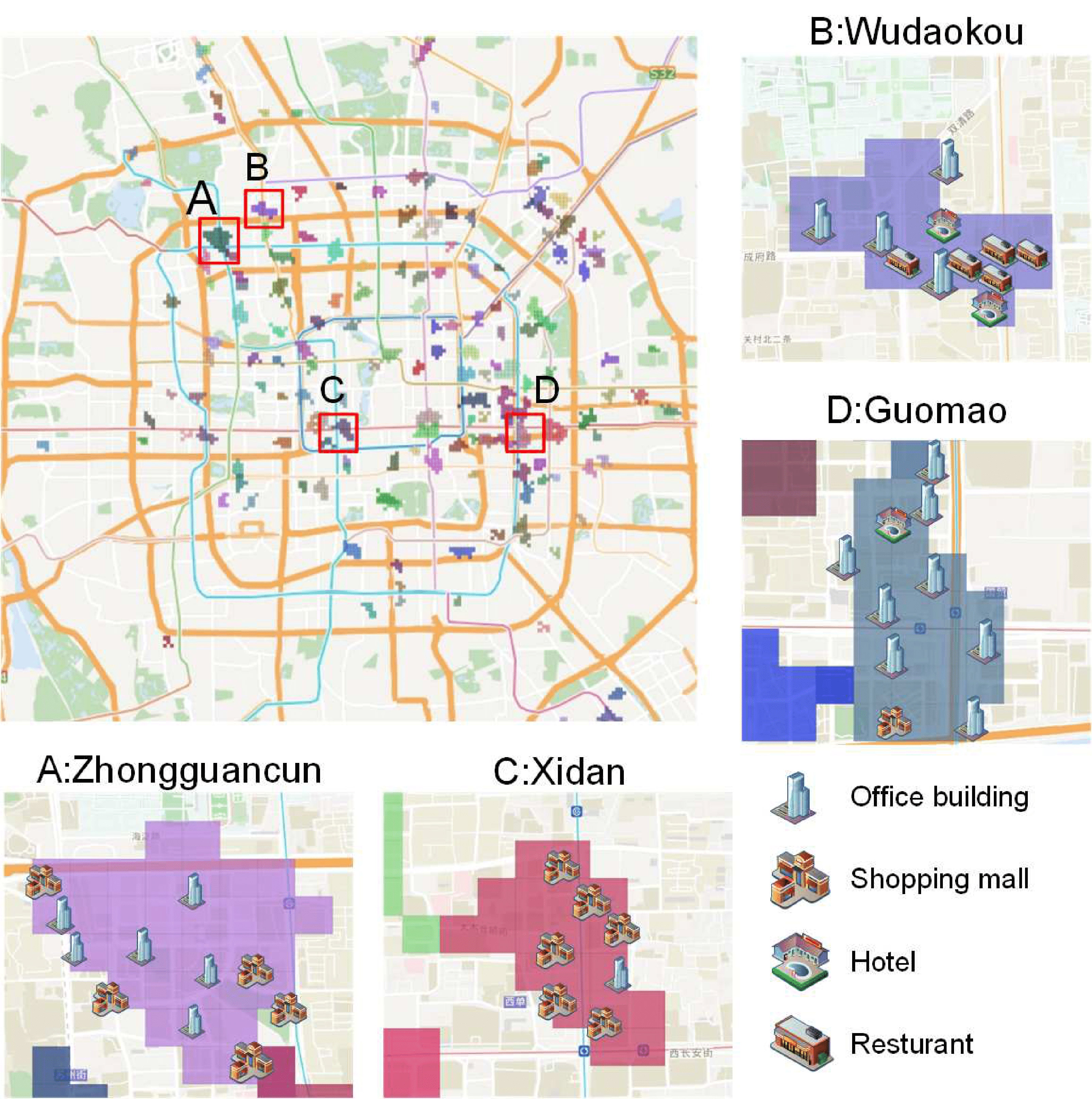 |
Urban Region-of-Interest (ROI) refers to the integrated urban areas with specific functionalities that attract people's attentions and activities, such as the recreational business districts, transportation hubs, and city landmarks. Indeed, at the macro level, ROI is one of the representatives for agglomeration economies, and plays an important role in urban business planning. At the micro level, ROI provides a useful venue for understanding the urban lives, demands and mobilities of people. However, due to the vague and diversified nature of ROI, it still lacks of quantitative ways to investigate ROIs in a holistic manner.
To this end, in this paper we propose a systematic study on ROI analysis through mining the large-scale online map query logs, which provides a new data-driven research paradigm for ROI detection and profiling. Specifically, we first divide the urban area into small region grids, and calculate their PageRank value as visiting popularity based on the transition information extracted from map queries. Then, we propose a density-based clustering method for merging neighboring region grids with high popularity into integrated ROIs. After that, to further explore the profiles of different ROIs, we develop a spatial-temporal latent factor model URPTM (Urban Roi Profiling Topic Model) to identify the latent travel patterns and Point-of-Interest (POI) demands of ROI visitors.
We implement extensive experiments to empirically evaluate our approaches based on the large-scale real-world data collected from Beijing. Indeed, by visualizing the results obtained from URPTM, we can successfully obtain many meaningful travel patterns and interesting discoveries on urban lives.
|
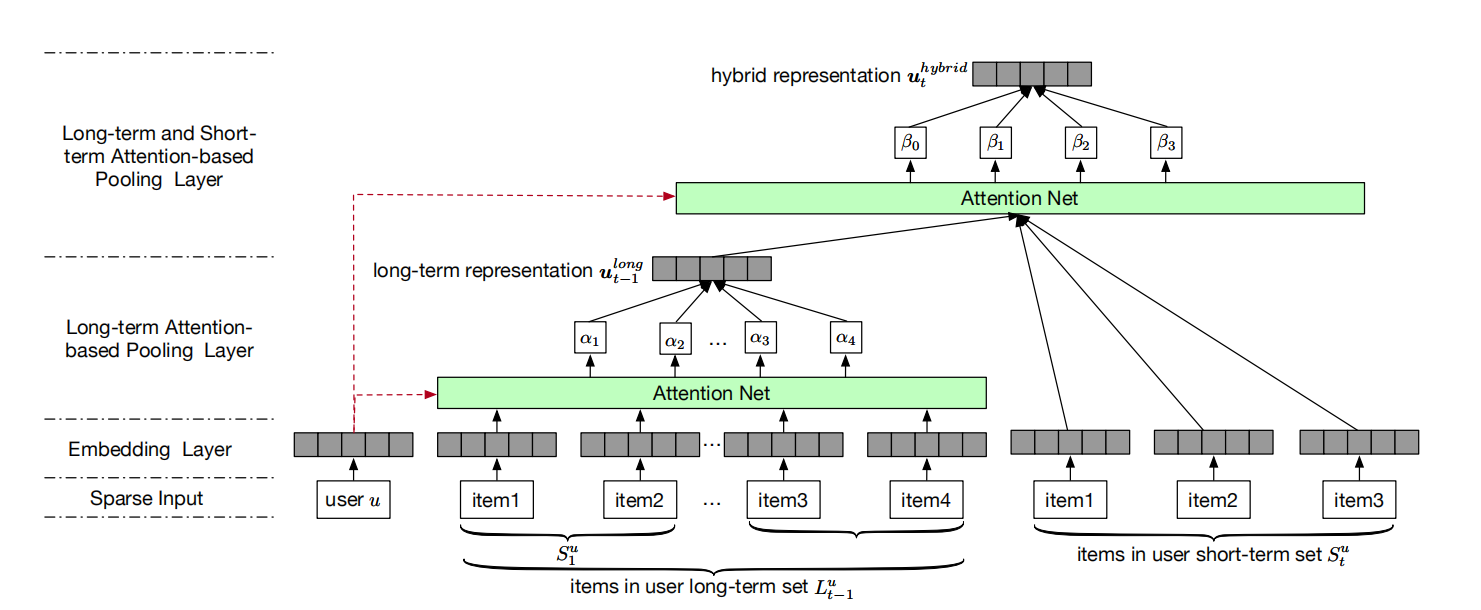
Haochao Ying , Fuzhen Zhuang , Fuzheng Zhang , Yanchi Liu , Guandong Xu , Xing Xie , Hui Xiong , Jian Wu : Sequential Recommender System based on Hierarchical Attention Networks. IJCAI 2018.
With a large amount of user activity data accumulated, it is crucial to exploit user sequential behavior for sequential recommendations. Conventionally, user general taste and recent demand are combined to promote recommendation performances.
However, existing methods often neglect that user
long-term preference keep evolving over time, and
building a static representation for user general
taste may not adequately reflect the dynamic characters. Moreover, they integrate user-item or itemitem interactions through a linear way which limits the capability of model. To this end, in this
paper, we propose a novel two-layer hierarchical
attention network, which takes the above properties into account, to recommend the next item user
might be interested. Specifically, the first attention
layer learns user long-term preferences based on
the historical purchased item representation, while
the second one outputs final user representation
through coupling user long-term and short-term
preferences. The experimental study demonstrates
the superiority of our method compared with other
state-of-the-art ones.
|
 |
Jingwu Chen , Fuzhen Zhuang , Xin Hong , Xiang Ao , Xing Xie , Qing He : Attention-driven Factor Model for Explainable Personalized Recommendation. SIGIR 2018
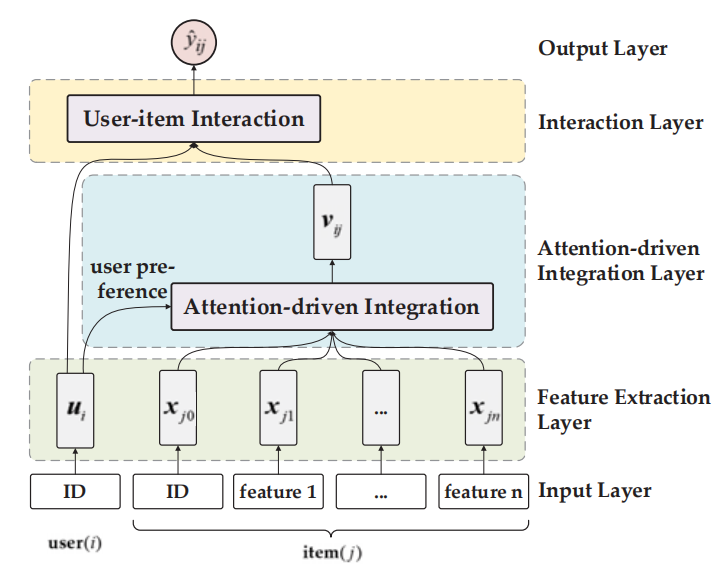 |
Latent Factor Models (LFMs) based on Collaborative Filtering (CF)
have been widely applied in many recommendation systems, due to
their good performance of prediction accuracy. In addition to users’
ratings, auxiliary information such as item features is often used to
improve performance, especially when ratings are very sparse. To
the best of our knowledge, most existing LFMs integrate different
item features in the same way for all users. Nevertheless, the attention on different item attributes varies a lot from user to user. For
personalized recommendation, it is valuable to know what feature
of an item a user cares most about. Besides, the latent vectors used
to represent users or items in LFMs have few explicit meanings,
which makes it difficult to explain why an item is recommended to
a specific user. In this work, we propose the Attention-driven Factor
Model (AFM), which can not only integrate item features driven
by users’ attention but also help answer this "why". To estimate
users’ attention distributions on different item features, we propose
the Gated Attention Units (GAUs) for AFM. The GAUs make it
possible to let the latent factors "talk", by generating user attention
distributions from user latent vectors. With users’ attention distributions, we can tune the weights of item features for different users.
Moreover, users’ attention distributions can also serve as explanations for our recommendations. Experiments on several real-world
datasets demonstrate the advantages of AFM (using GAUs) over
competitive baseline algorithms on rating prediction.
|
|



















